In this Article we will discuss about the your upcoming exam of Computer Subject Class 6 so you need Computer notes and Full syllabus topic wise brief.
Computer Class 6 (VI) Syllabus
- Computer Basics
- Introduction to Windows
- Introduction to Logo
- Using Paint Brush
- Notepad
- Microsoft Word
Computer Basics
What is Computer
A computer is an electronic device which takes input data processes it and returns the required output data. A computer comprises two components. These are Hardware and Software. Hardware is the physical part of the computer system.
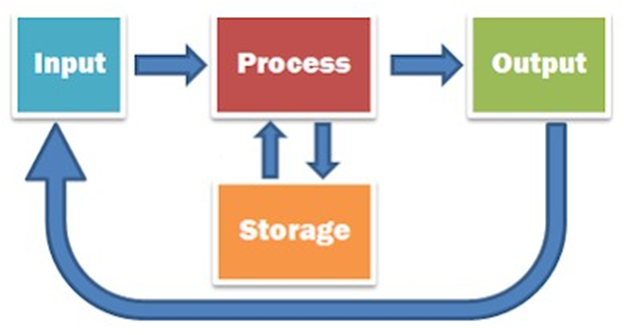
The basic parts without which a computer cannot work are as follows:
- Processor: It executes instructions from software and hardware.
- Memory: It is the primary memory for data transfer between the CPU and storage.
- Motherboard: It is the part that connects all other parts or components of a computer.
- Storage Device: It permanently stores the data, e.g., hard drive.
- Input Device: It allows you to communicate with the computer or to input data, e.g., a keyboard.
- Output Device: It enables you to see the output, e.g., monitor.
Benefits of Computer
- Increases your productivity: A computer increases your productivity. For example, after having a basic understanding of a word processor, you can create, edit, store, and print the documents easily and quickly.
- Connects to the Internet: It connects you to the internet that allows you to send emails, browse content, gain information, use social media platforms, and more. By connecting to the internet, you can also connect to your long-distance friends and family members.
- Storage: A computer allows you to store a large amount of information, e.g., you can store your projects, ebooks, documents, movies, pictures, songs, and more.
- Organized Data and Information: It not only allows you to store data but also enables you to organize your data. For example, you can create different folders to store different data and information and thus can search for information easily and quickly.
- Improves your abilities: It helps write good English if you are not good at spelling and grammar. Similarly, if you are not good at math, and don’t have a great memory, you can use a computer to perform calculations and store the results.
- Assist the physically challenged: It can be used to help the physically challenged, e.g., Stephen Hawking, who was not able to speak used computer to speak. It also can be used to help blind people by installing special software to read what is on the screen.
- Keeps you entertained: You can use the computer to listen to songs, watch movies, play games and more.
The computer has become a part of our life. There are plenty of things that we do in a day are dependent on a computer. Some of the common examples are as follows:
- ATM: While withdrawing cash from an ATM, you are using a computer that enables the ATM to take instructions and dispense cash accordingly.
- Smartphone: The smartphone that we use throughout the day for calling, texting, browsing is itself a computer.
History of Computer
Abacus
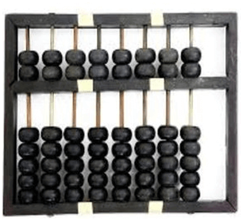
The history of computer begins with the birth of abacus which is believed to be the first computer. It is said that Chinese invented Abacus around 4,000 years ago.
It was a wooden rack which has metal rods with beads mounted on them. The beads were moved by the abacus operator according to some rules to perform arithmetic calculations. Abacus is still used in some countries like China, Russia and Japan. An image of this tool is shown below;
Napier’s Bones
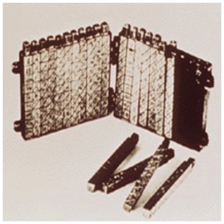
It was a manually-operated calculating device which was invented by John Napier (1550-1617) of Merchiston. In this calculating tool, he used 9 different ivory strips or bones marked with numbers to multiply and divide. So, the tool became known as “Napier’s Bones. It was also the first machine to use the decimal point.t
Pascaline

Pascaline is also known as Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine. It was invented between 1642 and 1644 by a French mathematician-philosopher Biaise Pascal. It is believed that it was the first mechanical and automatic calculator.
Pascal invented this machine to help his father, a tax accountant. It could only perform addition and subtraction. It was a wooden box with a series of gears and wheels. When a wheel is rotated one revolution, it rotates the neighboring wheel. A series of windows is given on the top of the wheels to read the totals. An image of this tool is shown below;
Stepped Reckoner or Leibnitz wheel

It was developed by a German mathematician-philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz in 1673. He improved Pascal’s invention to develop this machine. It was a digital mechanical calculator which was called the stepped reckoner as instead of gears it was made of fluted drums. See the following image;
Difference Engine

In the early 1820s, it was designed by Charles Babbage who is known as “Father of Modern Computer”. It was a mechanical computer which could perform simple calculations. It was a steam driven calculating machine designed to solve tables of numbers like logarithm tables.
Analytical Engine

This calculating machine was also developed by Charles Babbage in 1830. It was a mechanical computer that used punch-cards as input. It was capable of solving any mathematical problem and storing information as a permanent memory.
Tabulating Machine

It was invented in 1890, by Herman Hollerith, an American statistician. It was a mechanical tabulator based on punch cards. It could tabulate statistics and record or sort data or information. This machine was used in the 1890 U.S. Census. Hollerith also started the Hollerith?s Tabulating Machine Company which later became International Business Machine (IBM) in 1924.
Differential Analyzer

It was the first electronic computer introduced in the United States in 1930. It was an analog device invented by Vannevar Bush. This machine has vacuum tubes to switch electrical signals to perform calculations. It could do 25 calculations in few minutes.
Mark I

The next major changes in the history of computer began in 1937 when Howard Aiken planned to develop a machine that could perform calculations involving large numbers. In 1944, Mark I computer was built as a partnership between IBM and Harvard. It was the first programmable digital computer.
Components of a Computer
There are 5 main computer components that are given below:
- Input Devices
- CPU
- Output Devices
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
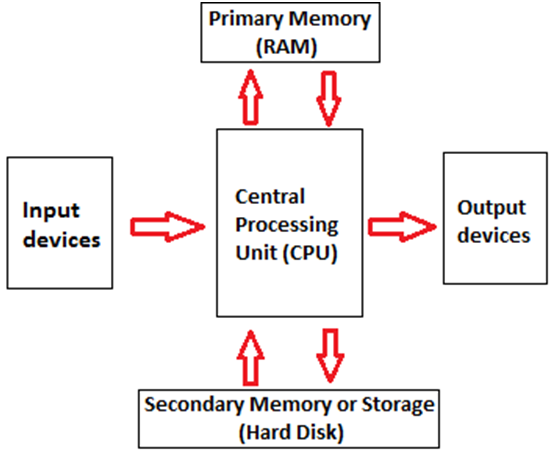
The operations of computer components are given below:
1) Inputting: It is the process of entering raw data, instructions and information into the computer. It is performed with the help of input devices.
2) Storing: The computer has primary memory and secondary storage to store data and instructions. It stores the data before sending it to CPU for processing and also stores the processed data before displaying it as output.
3) Processing: It is the process of converting the raw data into useful information. This process is performed by the CPU of the computer. It takes the raw data from storage, processes it and then sends back the processed data to storage.
4) Outputting: It is the process of presenting the processed data through output devices like monitor, printer and speakers.
5) Controlling: This operation is performed by the control unit that is part of CPU. The control unit ensures that all basic operations are executed in a right manner and sequence.
Features of Computer
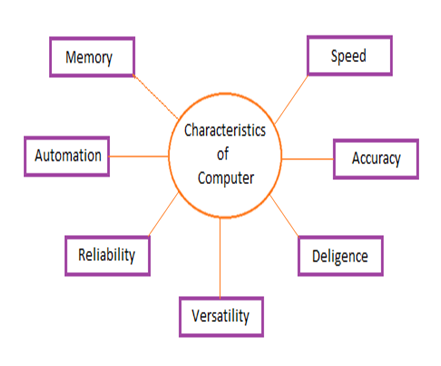
Speed
A computer works with much higher speed and accuracy compared to humans while performing mathematical calculations. Computers can process millions (1,000,000) of instructions per second. The time taken by computers for their operations is microseconds and nanoseconds.
Accuracy
Computers perform calculations with 100% accuracy. Errors may occur due to data inconsistency or inaccuracy.
Diligence
A computer can perform millions of tasks or calculations with the same consistency and accuracy. It doesn’t feel any fatigue or lack of concentration. Its memory also makes it superior to that of human beings.
Versatility
Versatility refers to the capability of a computer to perform different kinds of works with same accuracy and efficiency.
Reliability
A computer is reliable as it gives consistent result for similar set of data i.e., if we give same set of input any number of times, we will get the same result.
Automation
Computer performs all the tasks automatically i.e. it performs tasks without manual intervention.
Memory
A computer has built-in memory called primary memory where it stores data. Secondary storage are removable devices such as CDs, pen drives, etc., which are also used to store data.
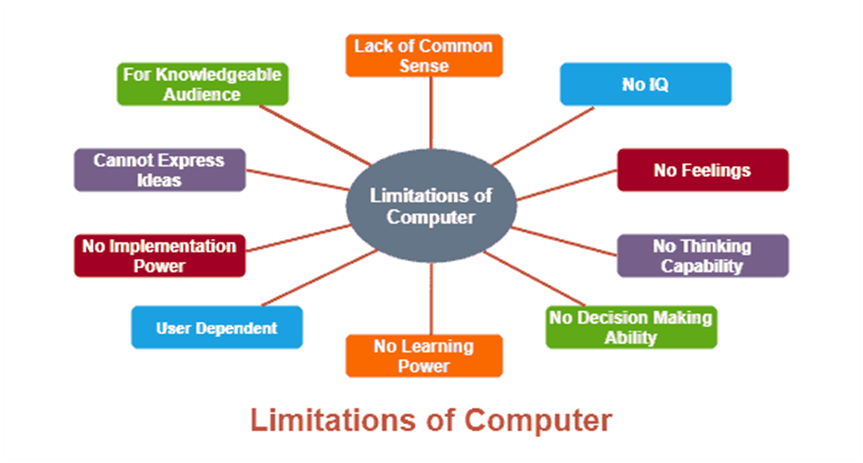
Limitation of Computer
Computer Memory
The computer memory holds the data and instructions needed to process raw data and produce output. The computer memory is divided into large number of small parts known as cells. Each cell has a unique address which varies from 0 to memory size minus one.
Computer memory is of two types: Volatile (RAM) and Non-volatile (ROM). The secondary memory (hard disk) is referred as storage not memory.
But, if we categorize memory on behalf of space or location, it is of four types:
- Register memory
- Cache memory
- Primary memory
- Secondary memory
Cache memory is a high-speed memory, which is small in size but faster than the main memory (RAM). The CPU can access it more quickly than the primary memory. So, it is used to synchronize with high-speed CPU and to improve its performance.
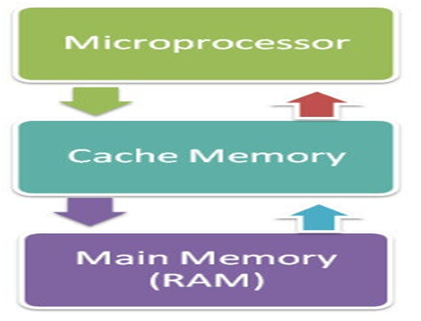
Primary Memory
Primary Memory is of two types: RAM and ROM.
RAM (Volatile Memory)
It is a volatile memory. It means it does not store data or instructions permanently. When you switch on the computer the data and instructions from the hard disk are stored in RAM.
CPU utilizes this data to perform the required tasks. As soon as you shut down the computer the RAM loses all the data.
ROM (Non-volatile Memory)
It is a non-volatile memory. It means it does not lose its data or programs that are written on it at the time of manufacture. So it is a permanent memory that contains all important data and instructions needed to perform important tasks like the boot process.
Secondary Memory
The secondary storage devices which are built into the computer or connected to the computer are known as a secondary memory of the computer. It is also known as external memory or auxiliary storage.
The secondary memory is accessed indirectly via input/output operations. It is non-volatile, so permanently stores the data even when the computer is turned off or until this data is overwritten or deleted. The CPU can’t directly access the secondary memory. First, the secondary memory data is transferred to primary memory then the CPU can access it.
What is Printer?
A printer is a hardware output device that is used to generate hard copy and print any document. A document can be of any type such as a text file, image, or the combination of both. It accepts input command by users on a computer or on other devices to print the documents. For example, if you have to submit a project report at your college, you need to create a soft copy of your report and print it with the help of the printer.

Printers are one of the common computer peripheral devices that can be classified into two categories that are 2D and 3D printers. The 2D printers are used to print text and graphics on a paper, and 3D printers are used to create three dimensional physical objects.
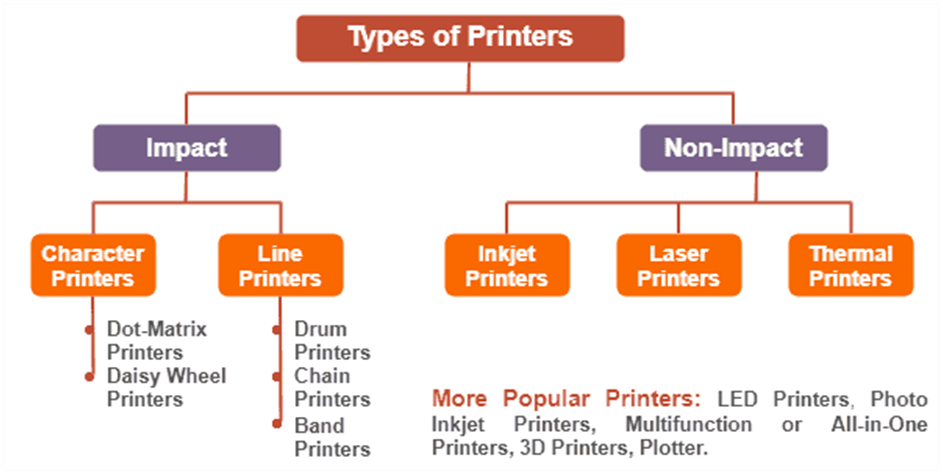
Types of printer
Although there are different types of printers, nowadays, two types of printers are commonly used, which are inkjet and laser printers. A list of all the various types of printers is given below:
- Inkjet Printers
- Laser Printers
- 3D Printers
- LED Printers
- Solid Ink Printers
- Dot Matrix Printers
- Multifunction or All-in-One Printers
- Thermal printer
- Plotter
Generation of Computers
A generation of computers refers to the specific improvements in computer technology with time. In 1946, electronic pathways called circuits were developed to perform the counting. It replaced the gears and other mechanical parts used for counting in previous computing machines.
In each new generation, the circuits became smaller and more advanced than the previous generation circuits. The miniaturization helped increase the speed, memory and power of computers. There are five generations of computers which are described below;
First Generation Computers
The first generation (1946-1959) computers were slow, huge and expensive. In these computers, vacuum tubes were used as the basic components of CPU and memory. These computers were mainly depended on batch operating system and punch cards. Magnetic tape and paper tape were used as output and input devices in this generation;
Some of the popular first generation computers are;
- ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
- EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)
- UNIVACI (Universal Automatic Computer)
- IBM-701
- IBM-650
Second Generation Computers
The second generation (1959-1965) was the era of the transistor computers. These computers used transistors which were cheap, compact and consuming less power; it made transistor computers faster than the first generation computers.
In this generation, magnetic cores were used as the primary memory and magnetic disc and tapes were used as the secondary storage. Assembly language and programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN, and Batch processing and multiprogramming operating systems were used in these computers.
Some of the popular second generation computers are;
- IBM 1620
- IBM 7094
- CDC 1604
- CDC 3600
- UNIVAC 1108
Third Generation Computers
The third generation computers used integrated circuits (ICs) instead of transistors. A single IC can pack huge number of transistors which increased the power of a computer and reduced the cost. The computers also became more reliable, efficient and smaller in size. These generation computers used remote processing, time-sharing, multi programming as operating system. Also, the high-level programming languages like FORTRON-II TO IV, COBOL, PASCAL PL/1, ALGOL-68 were used in this generation.
Some of the popular third generation computers are;
- IBM-360 series
- Honeywell-6000 series
- PDP (Personal Data Processor)
- IBM-370/168
- TDC-316
Fourth Generation Computers
The fourth generation (1971-1980) computers used very large scale integrated (VLSI) circuits; a chip containing millions of transistors and other circuit elements. These chips made this generation computer more compact, powerful, fast and affordable. These generation computers used real time, time sharing and distributed operating system. The programming languages like C, C++, DBASE were also used in this generation.
Some of the popular fourth generation computers are;
- DEC 10
- STAR 1000
- PDP 11
- CRAY-1(Super Computer)
- CRAY-X-MP (Super Computer)
Fifth Generation Computers
In fifth generation (1980-till date) computers, the VLSI technology was replaced with ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration). It made possible the production of microprocessor chips with ten million electronic components. This generation computer used parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software. The programming languages used in this generation were C, C++, Java, .Net, etc.
Some of the popular fifth generation computers are;
- Desktop
- Laptop
- Notebook
- Ultrabook
- Chromebook
Introduction to Windows
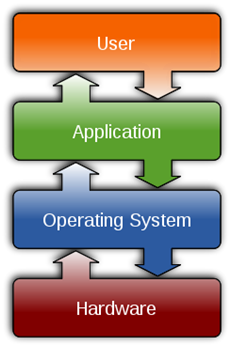
- Operating system
- The operating system is the most important program
that runs on a computer.
- Operating system is an interface between computer and user.
- It is responsible for the management and coordination of activities and the sharing of the resources of the computer.
Types of Operating System
- Real-time
- Multi-user vs.Single-user
- Multi-tasking vs.Single-tasking
- Distributed
- Embedded
Major Functions of Operating System
Standard Means of Communication between User and Computer
- The OS also establishes a standard means of communication between users and their computer systems.
- It does this by providing a user interface and a standard set of commands that control the hardware.
User Interface
- A program that controls a display for the user (usually on a computer monitor) and that allows the user to interact with the system).
- The user interface allows the user to communicate with the operatingsystem.
User Interface
- The user interface provides means of:
- Input – allowing the users to manipulate a system
- Output – allowing the system to indicate the effects of the users’ manipulation.
Types of User Interface
- Command lineinterface
- Graphical userinterface
Examples of Operating System
- MS-DOS
- Windows
- MacOS
- Linux
- Solaris
- Android
List of Common Operating Systems
Given below is a list of commonly used Operating systems along with their year of release.
| List of Operating Systems | |
| Name of the OS | Release Date |
| Android | 2008 |
| iOS | 2007 |
| Windows | 1985 |
| Mac OS | 2001 |
| MS-DOS | 1981 |
| Chrome OS | 2011 |
| Windows Phone | 2010 |
| Blackberry OS | 1999 |
| Firefox OS | 2013 |
Introduction to Notepad
Introduction to Logo
Logo is a programming language that is very simple and easy to learn. It is used for teaching students and children how to program a computer.
Why should we learn the Logo language?
- Because it is fun, lots of fun.
- Enhances the logical sense of the children.
- Develops programming skills.
- It is real Computer Science.
Logo is a very easy and interesting programming language to learn. It has enough depth to virtually do anything, which can be done in any other computer programming language.
- The Turtle Logo’s Prompt
The MSW Logo screen has two parts −
- A Drawing window above with a triangle-shaped TURTLE in the center.
- A Commander window as shown in the following screenshot.
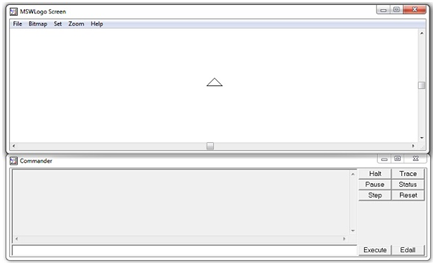
We will write commands in the command line, i.e., the text box at the bottom of the Commander Window. To execute or run these commands, press Enter or click the Execute Button. We can also write and run more than one command online at a time.
The command history will appear in the gray box. Click a line in the history to make it jump to the respective command line, then we can make changes (if required). Once this is done, press Enter or click the Execute Button.
The simple Logo Drawing Commands move the Turtle forward and backward and also turn it right or left. The commands and their abbreviations are given below −
- fd – forward
- bk – backward
- rt – right
- lt – left
- cs – clearscreen
MS Paint
Microsoft Word
MS-WORD
MS Word is a word processing software. It falls under the category of application software. It is used to create and edit personal and business documents such as letters, reports etc. The default file extension of MS Word 2007 is .docx. Given below is the basic Window that appears when we open the MS Word –

Some of the important shortcuts are given below:
- Open a file – CTRL +O
- Create a new document – CTRL +N
- Close a document – CTRL + W
- Save a file – CTRL +S
- Display the ‘Save as’ dialog box –F12
- Copy – CTRL +C
- Paste – CTRL +V
- Cut – CTRL +X
- Undo – CTRL +Z
- Redo or repeat an action – CTRL +Y
- Cancel an action – ESC
Also You Can Download Android application for the Computer Class 6
Android Application

